Documentation
About Kubeapps
Tutorials
How-to guides
Step 3: Add Application Repositories to Kubeapps ¶
Once Kubeapps is up and running on the VMware Tanzu™ Kubernetes Grid™ cluster, the next step is to add application repositories to it. This could include public repositories, private repositories or both.
The general procedure to add any repository is described below:
Log in to Kubeapps as described in the previous step.
Click the right menu button in the top right corner (dotted square).
Click the Package Repositories option in the right menu to navigate to the
Package Repositoriespage.
Add a new repository by clicking the Add Package Repository button.
NOTE: If no repositories were specified in the
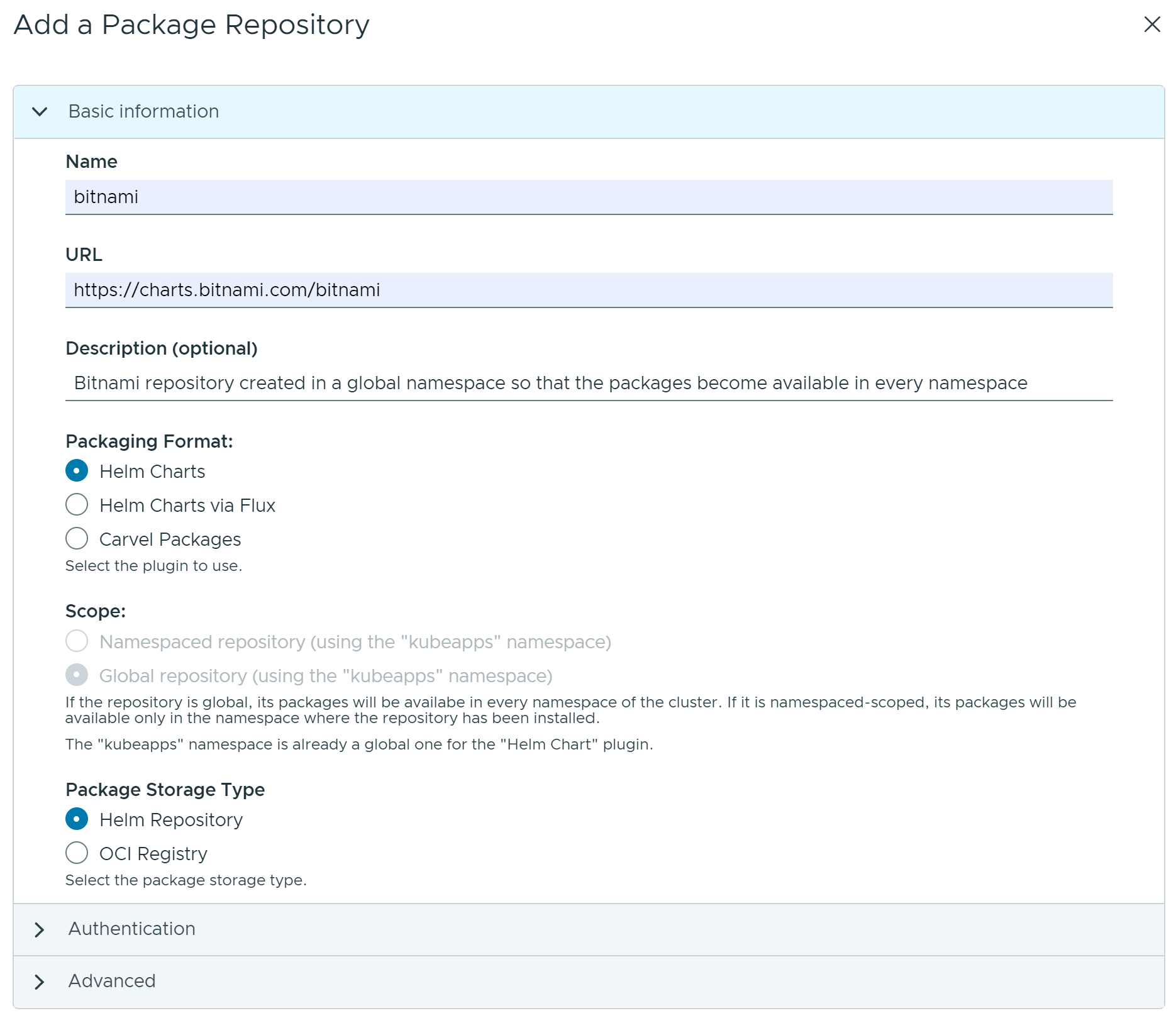
initialReposchart parameter during the Kubeapps installation, no repositories are displayed on thePackage Repositoriespage.Fill the Add a Package Repository form using the guidelines below:
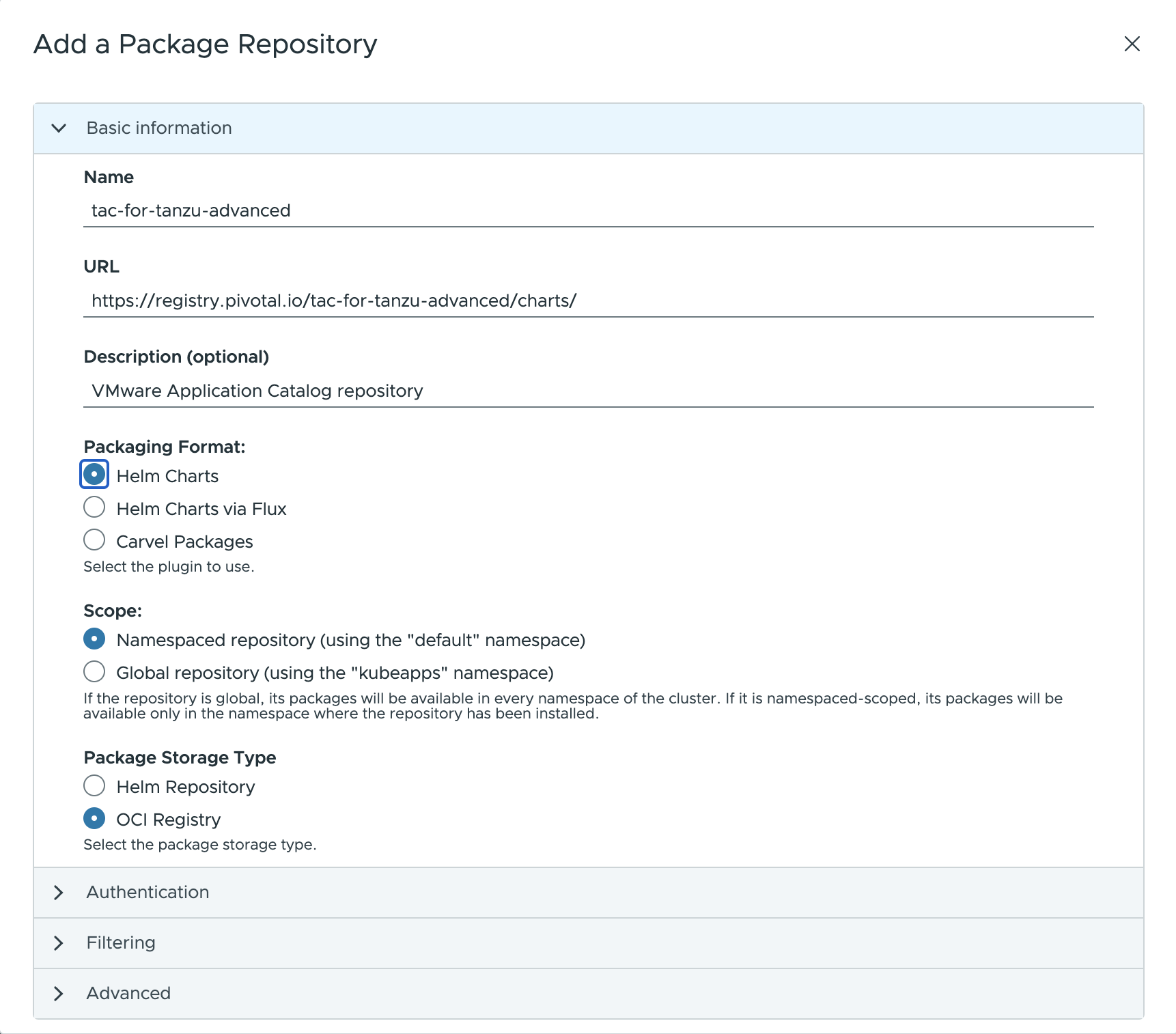
Namefield is a friendly display name for the repository.URLfield specifies the endpoint of the repository. This endpoint might require different forms of authentication, such asNone,Basic Auth(username and password),Bearer Token(a token) or anotherCustommechanism.Descriptionfield (optional) is a brief summary for the repository.Packaging formatfield specifies the format of the packages available in the repository.Scopefield specifies where the packages from the repository could be installed in the cluster (globally on any namespace or limited to an specific namespace in the cluster).Package Storage Typefield specifies the type of repository. Currently, Kubeapps supports both Helm repositories and OCI registries.
Repository Authorizationfield provides additional credentials for pulling the container images from a registry. When selecting theDocker Registryas theRepository Authorization, this field is required. Whereas this value usually is the same as the one used in the `Docker Registry, it is possible to create a fresh secret or choose an existing one.
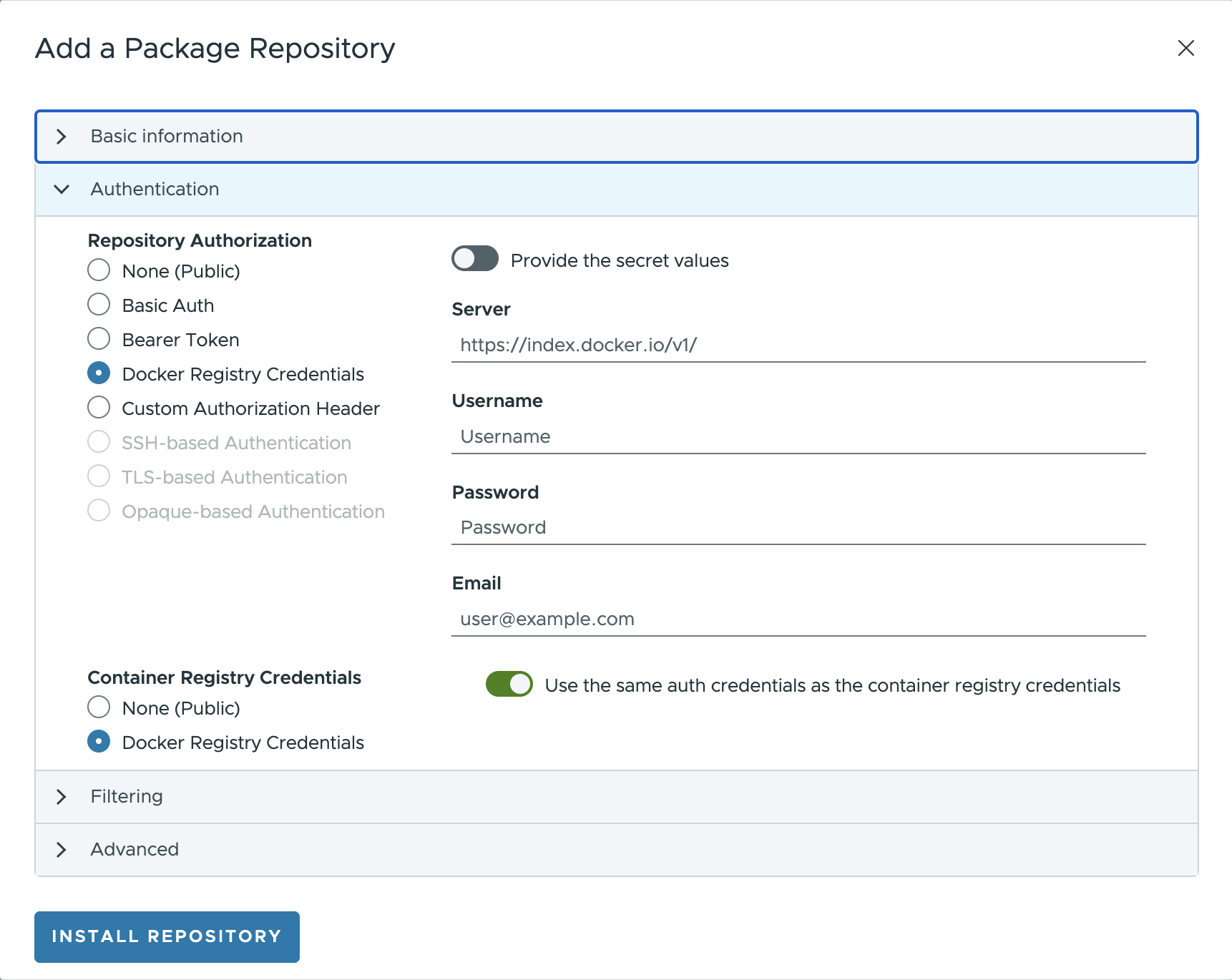
- For OCI registries, when using the Helm plugin, it is necessary to also manually specify the list of OCI artifacts to fetch in the List of Repositories field (as there is no standard index yet). Additionally, artifacts can be excluded using regular expressions if required.
Click the Install Repository button to finish the process and add the repository to Kubeapps.
Retrieving the catalog from the repository takes a few minutes. Once complete, the contents of the repository become available in Kubeapps.
The following sections demonstrate the process of filling the Add a Package Repository form for two specific examples: VMware Marketplace™ and VMware Tanzu™ Application Catalog™ for Tanzu™ Advanced.
Add the VMware Marketplace™ ¶
NOTE: This repository is currently under heavy development. Therefore, the URL used below is subject to change.
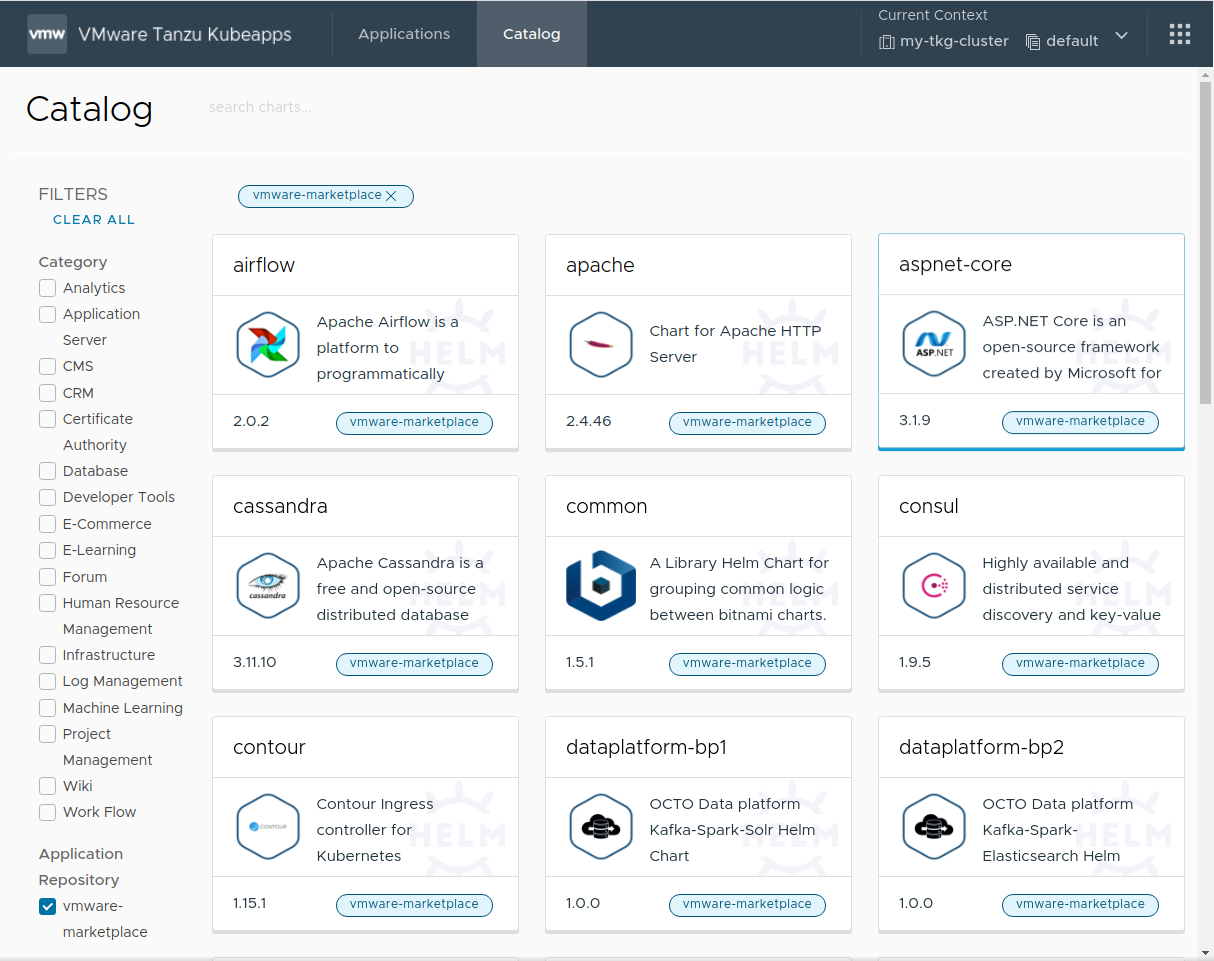
The public content from the VMware Marketplace™ repository can be retrieved at https://charts.market.csp.vmware.com/bitnami. Since this is a public repository, it is only necessary to configure the following values in the Add a Package Repository form:
Name: Add a descriptive name, such asvmware-marketplace.URL: Use the endpoint URLhttps://charts.market.csp.vmware.com/bitnami.Packaging format: useHelm Charts.Repository Authorization: leave by default asNone.- Leave the rest of the fields as set by default.
Once completed, the public catalog is available in Kubeapps, as shown below:
Add the VMware Tanzu™ Application Catalog™ for Tanzu™ Advanced ¶
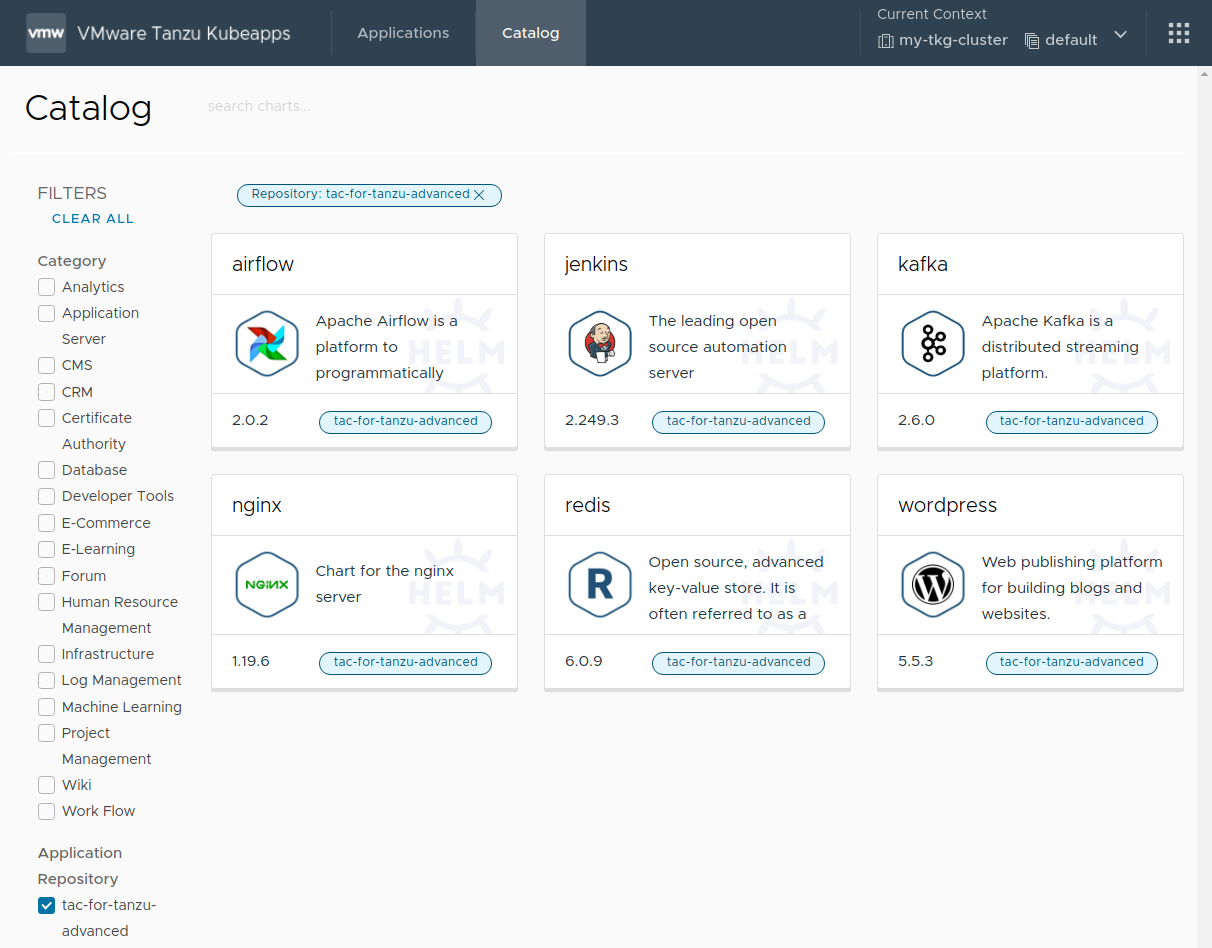
The private content from the VMware Tanzu™ Application Catalog™ for Tanzu™ Advanced repository can be retrieved at https://registry.pivotal.io/tac-for-tanzu-advanced/charts/. Since this is a private OCI registry, there are two key differences to note in the process:
- It is necessary to specify repository authentication credentials using the
Basic Authoption and defining the correct username and password. If you do not have these credentials, please reach out to your VMware sales representative . - As this is an OCI registry, it is necessary to manually add the list of artifacts to be retrieved in the
List of Repositoriesfield.
Configure the following values in the Add Package Repository form:
Name: Add a descriptive name, such astac-for-tanzu-advanced.URL: Use the endpoint URLhttps://registry.pivotal.io/tac-for-tanzu-advanced/charts/.Packaging format: useHelm Charts.Repository TypeSet the value toOCI Registry.
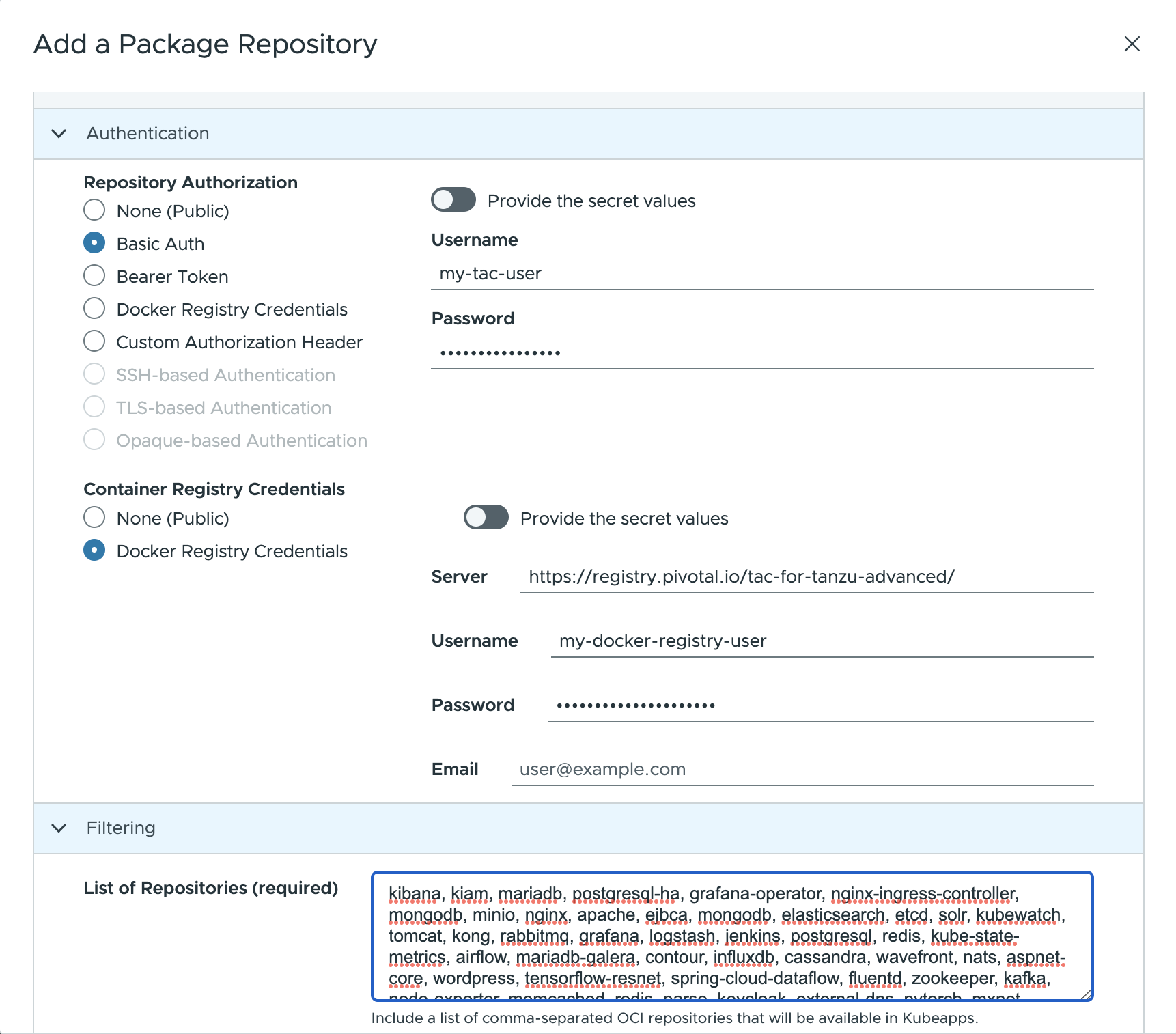
Repository Authorization: Set the value toBasic Authand enter your VMware Tanzu™ Application Catalog™ for Tanzu™ Advanced username and token in theUsernameandPasswordfields respectively.Container Registry Credentials: Set the value toDocker Registry Credentialsand provide the following info (optionally you can use an existing secret):- Server: Set the value to
https://registry.pivotal.io/tac-for-tanzu-advanced/. - Username: Set the value to your VMware Tanzu™ Application Catalog™ for Tanzu™ Advanced username.
- Password: Set the value to your VMware Tanzu™ Application Catalog™ for Tanzu™ Advanced token.
- Server: Set the value to
List of Repositories: Set the value tokibana, kiam, mariadb, postgresql-ha, grafana-operator, nginx-ingress-controller, mongodb, minio, nginx, apache, ejbca, mongodb, elasticsearch, etcd, solr, kubewatch, tomcat, kong, rabbitmq, grafana, logstash, jenkins, postgresql, redis, kube-state-metrics, airflow, mariadb-galera, contour, influxdb, cassandra, wavefront, nats, aspnet-core, wordpress, tensorflow-resnet, spring-cloud-dataflow, fluentd, zookeeper, kafka, node-exporter, memcached, redis, parse, keycloak, external-dns, pytorch, mxnet, harbor, thanos, spark, consul, kubeapps, mysql, wildfly, metrics-server.
NOTE: To obtain the most current list of repositories, log in to the registry using the
orastool and run the command below:oras pull registry.pivotal.io/tac-for-tanzu-advanced/index:latest -a && cat asset-index.json | jq -r '.charts | map(.name) | join(",")'
Once complete, the private catalog is available in Kubeapps, as shown below:
At the end of this step, the Kubeapps installation is configured with one or more application repositories. The next step is to start using Kubeapps .
Tutorial index ¶
- Step 1: Configure an Identity Management Provider in the Cluster
- Step 2: Configure and Install Kubeapps
- Step 3: Add Application Repositories to Kubeapps
- Step 4: Deploy and Manage Applications with Kubeapps
Appendix: Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) in Application Repositories ¶
A Kubeapps application repository can be created by anyone with the required RBAC privileges for that namespace.
Users with cluster-wide RBAC privileges for creating application repositories can still create an application repository whose charts are available to users in all namespaces by selecting All Namespaces when creating the repository.
To grant a user permission to create AppRepository objects in a specific namespace, create RoleBinding objects associating apprepositories-read and apprepositories-write roles with that user, as shown below. Replace the USERNAME and CUSTOM-NAMESPACE placeholders with the corresponding username and namespace name.
TIP: If users only require permissions to deploy charts from application repositories in a specific namespace, it is sufficient to create only the
apprepositories-readRoleBindingobject.
# Grant the user USERNAME read apprepositories permissions on the CUSTOM-NAMESPACE namespace
kubectl -n CUSTOM-NAMESPACE create rolebinding USERNAME-apprepositories-read \
--user USERNAME
--clusterrole kubeapps:$KUBEAPPS_NAMESPACE:apprepositories-read
# Grant the user USERNAME write apprepositories permissions on the CUSTOM-NAMESPACE namespace
kubectl -n CUSTOM-NAMESPACE create rolebinding USERNAME-apprepositories-write \
--user USERNAME \
--clusterrole kubeapps:$KUBEAPPS_NAMESPACE:apprepositories-write

 Slack
Slack GitHub
GitHub X
X